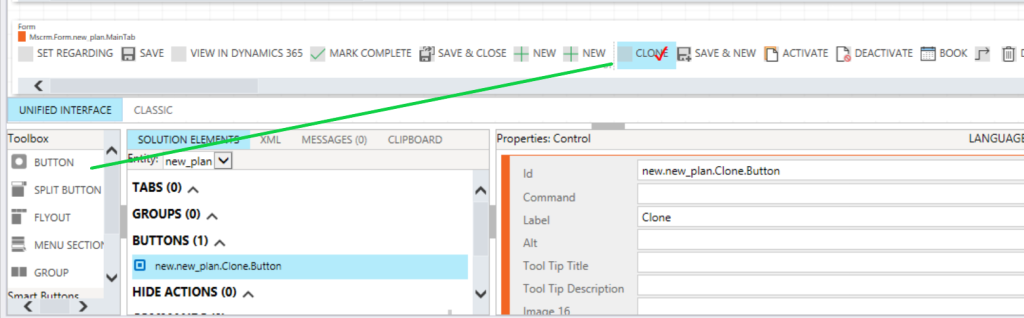
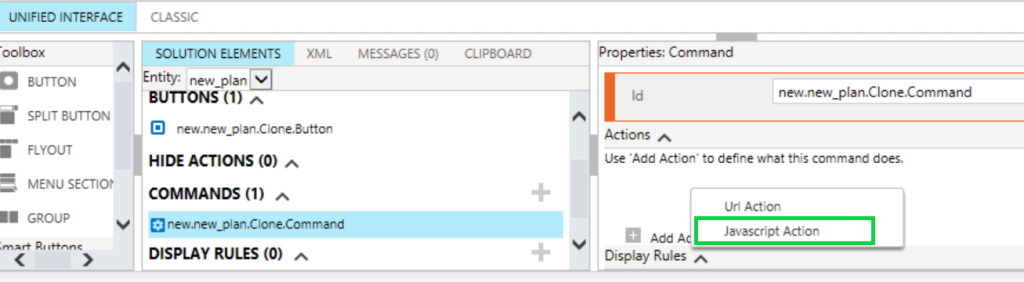
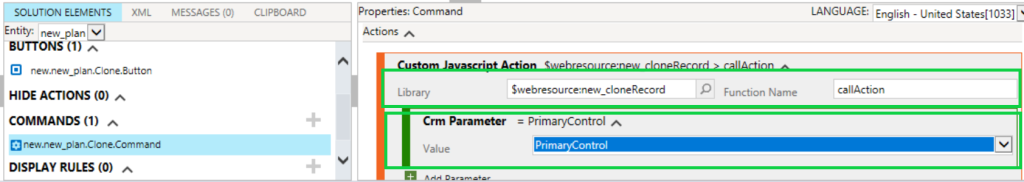
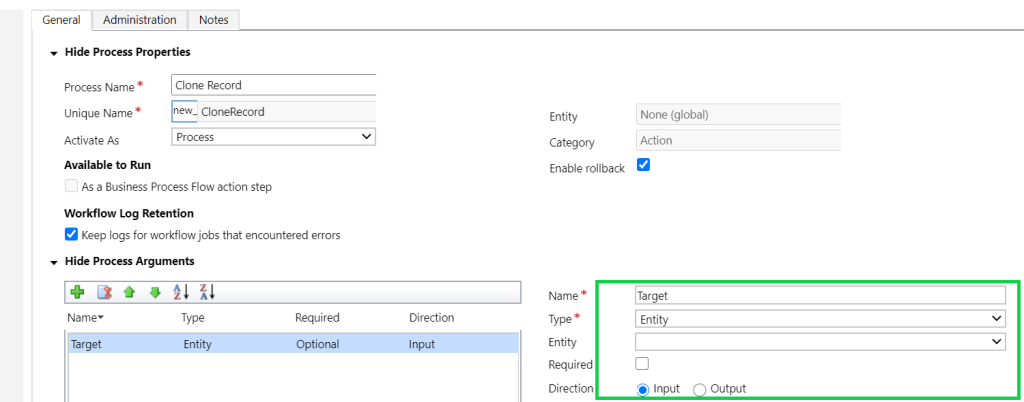
Here we will discuss below points regarding CRM plugins.
- Plugin Concept
- Sample Task
- Build, Deploy & Debug, Test
- Release
- Best Practice
- Exception handling
Plugin Concept
- Plugins are custom business logic or code which modifies the default behavior of CRM platform.
- This requires .net c# programming concept and a developer knowledge with CRM SDK knowledge.
- As a technical term Plugin is a .net class library(.dll) which uses the reference of Microsoft.Xrm.Sdk.dll and Microsoft.Crm.Sdk.Proxy assembly to interact with CRM Organisation to achieve the task. You can find it in CRM SDK\bin folder which you can download Freely here by choosing correct version of CRM SDK.
- As plugin interacts with CRM service so System.Runtime.Serialization namespace is required.
- Plugin are also called as CRM Event Handlers which reacts on events raised by CRM platform. Events are like Create Record, Update Record, Retrieve Record, Delete Record etc..
- Plugins follow an Event Execution Pipeline model of CRM as snapshot given below.
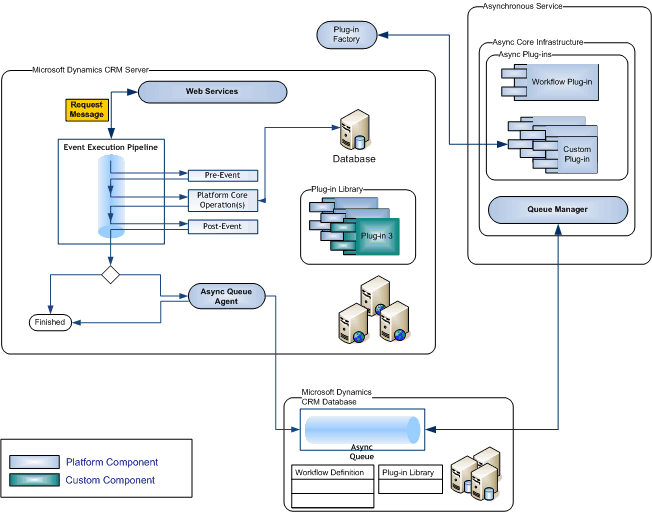
- CRM SDK also contains sample codes to refer for developers to start plugins. Also you can follow here to check out sample plugin code structure.
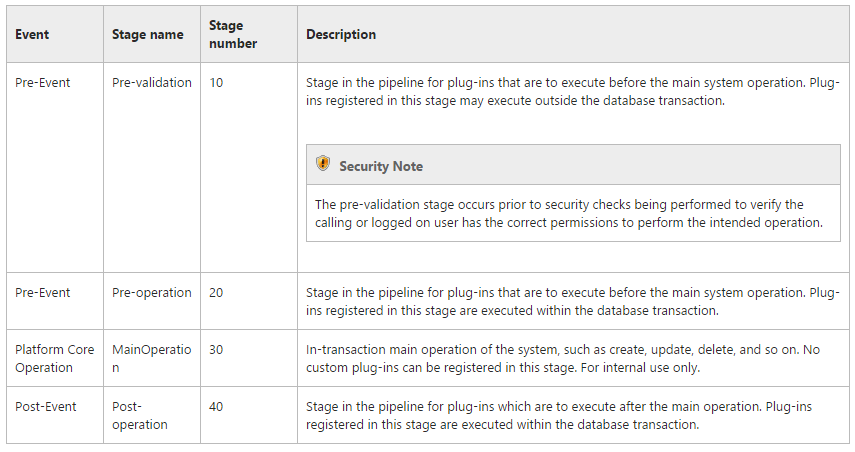
- Plugins can be registered in below Stages Pre-Validation, Pre-Operation, Post-Operation. But cannot be registered again main core operation. Checkout the below image for understanding the stages.
- As plugins are nothing but .net assemblies the output of the plugin is a .dll file. Plugins class implements an Interface called as IPlugin interface and the method Execute must be implemented which takes IServiceProvider parameter.
Plugin Context
- When a plug-in runs in response to an execution pipeline event for which it is registered, the plug-in’s Execute method is called. That method passes an IServiceProvider object as a parameter, which contains a number of useful objects.The sample is given below. to understand the context more checkout the topic here.
public class MyPlugin: IPlugin { public void Execute(IServiceProvider serviceProvider){ //code here} } - By the below code you can get the context from the service provider object.
// Obtain the execution context from the service provider. IPluginExecutionContext context = (IPluginExecutionContext) serviceProvider.GetService(typeof(IPluginExecutionContext)); - The context contains the Entity information on which it is being registered. The context has properties like InputParameters & OutPutParameters.
- When a plug-in runs in response to an execution pipeline event for which it is registered, the plug-in’s Execute method is called. That method passes an IServiceProvider object as a parameter, which contains a number of useful objects.The sample is given below. to understand the context more checkout the topic here.
Plugin Impersonation
- By default plugins are set to run as calling user but sometimes we run the plugins using System user with highest privilege this is called Impersonation in plugin.
- We can set Run in Context property for Plugins Impersonation while registering the plugin.
- on Impersonation in plugin Hosk has written a nice article check out here.
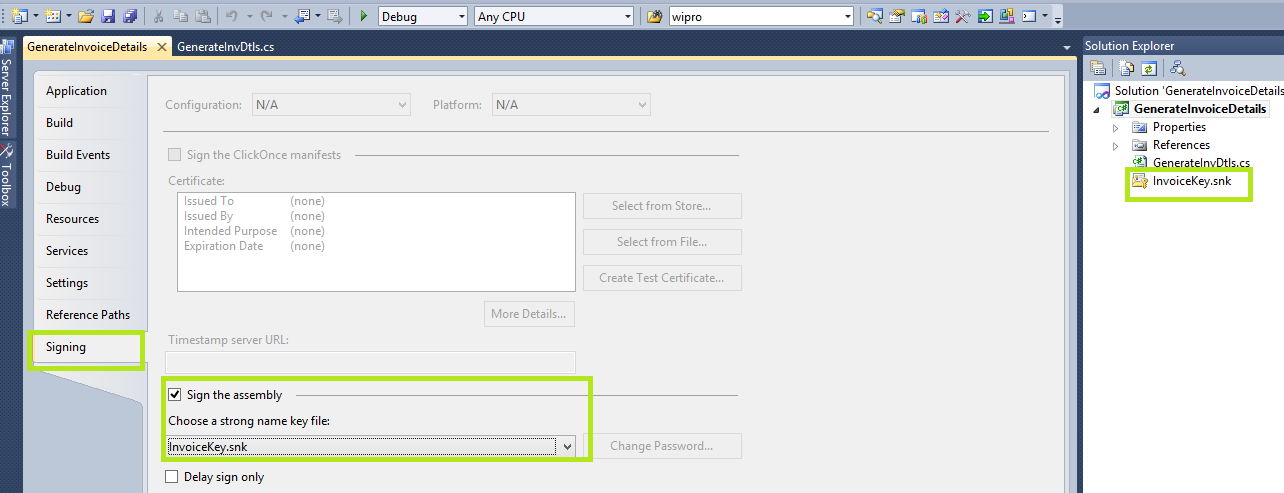
Signing the plugin assembly
- Every plugin must be signed by a Key. This signing process generates a certificate for the assembly.
- We can do this by the properties option of the plugin in Signing option.
Plugin registration tool
- Plugin registration tool is available in the CRM SDK folder. This tool provides a flexible way to register our plugins.
- In this tool we can set the message and add steps for the plugin assembly. Also we can set the Plugin execution order, Impersonation etc.
- Plugins and Custom Workflow activities both can be registered using this tool.
Privilege for Register
- Plugins can be developed by any user who know coding but to deploy or register the plugin in CRM you have to be added in the Deployment Manager group.
Plug-in isolation
- Plugins which are registered in isolation have no access to file system access and network access.
- Plugins which are targeted for online version of CRM must be registered in Isolation and for On-premise version the isolation is not required.
Shared variables
- Shared variables are the plugin variables which can be identified by multiple plugins. Using this option we can pass data from one plugin to another.
- A Pre-operation registered plugin can send data to a post-operation registered plugin using shared variables.
Messages
- Messages are nothing but events that are raised in CRM platform. There is an exhaustive list of events that are generated in CRM. The list is given in CRM SDK for reference.
- Images ( Pre & Post Images)
- Images are snapshots of the entity record. In CRM have two images type Pre and Post images.
- Pre-Image contains the record snapshot of the current data from database.
- Post-Image is the snapshot of the updated and recent data passed in the context.
- There is no Pre-Image for a Create event.
- There is no Post-Image for a Delete event.
- For an Update event we have both Pre and Post Images, we can configure this images in plugin registration tool while registering the plugin.
Sync/Async
- Plugins can be synchronous or asynchronous. synchronous plugins runs immediately and the processing system waits till the plugin completes execution so in this case user has to wait for the completion of plugin.
- Asynchronous plugins runs in background like workflows when the system is free.
2mins TimeOUT
- Plugins are developed to run as quick as possible. synchronous plugins are part of core operation thread so runs immediately and user has to wait till the plugin completes successfully.
- If the Plugin is developed with heavy and time consuming codes and it exceeds 2minutes then it fails executing throwing a TimeOUT error resulting the process roll back in that specific transaction.
- The plugin runs in one transaction so any error or exception rolls back the whole process.
- SO be careful while designing plugins considering its load and processing options.
Registration options
- Plugins can be registered in 3 locations
- Database : assembly stores in SQL organization database
- Disk : assembly will be stored in the Installation directory of CRM in Server\Bin
- GAC : Assembly will be stored in System Global Assembly Cache in windows.
- Plugins can be registered in 3 locations
Sample Task – Practical
Lets take a scenario and develop a plugin from scratch for a better understanding.
- Scenario
- Requirement
- Solution
Scenario: There is a Invoice entity with attributes (amount(money), terms(int), Invoiceday(int) ). There is another entity InvoiceDetail with attributes (amount(money), Invoicedate(datetime)).
Invoice (1) : Invoice Detail (N)
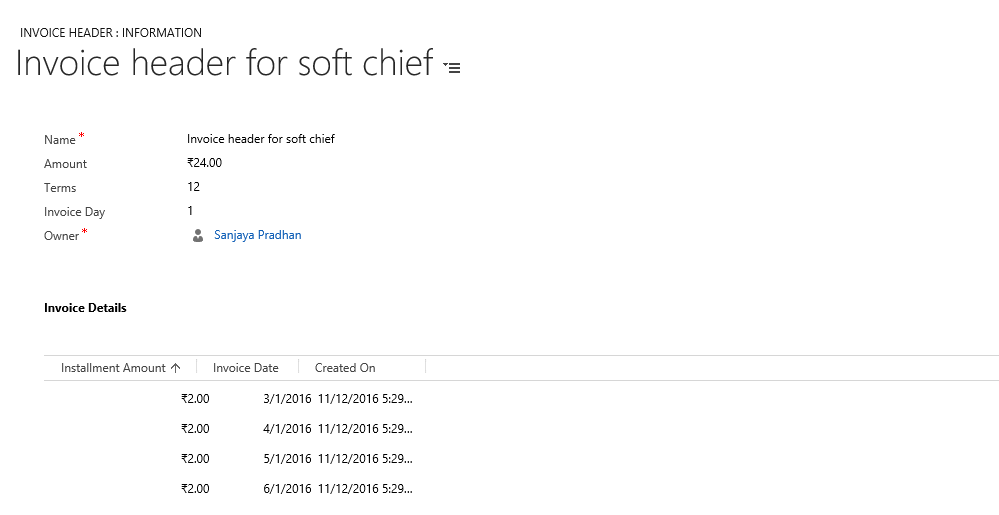
Requirement : When a user will create a Invoice record with all field values then terms field value number of Invoice detail records will be created.
E.g. :if terms =12, amount=24.00, invoiceday=1 then 12 payment detail records will be created with amount=2 i.e. (24/12), Invoicedate =1st of next month with year, accordingly upto 12 month.
Build, Deploy & Debug, Test
- References & SDK
- For building Plugins as discussed above download CRM SDK.
- Add required references to the plugin as specified above and refer the sample code folder of CRM SDK for more information.
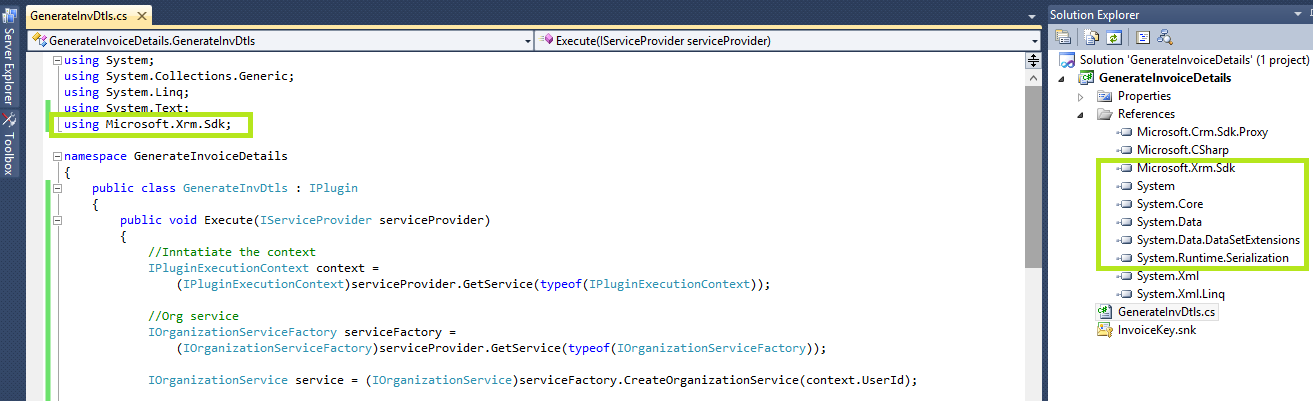
- Visual Studio Class library
- Plugin is nothing but a .net class library so the project type should be chosen as a Class library project.
- Set the .net framework correctly as given screenshot.
- Context Depth
- Sometimes Plugins executed for infinite loop so to stop the plugin running from infinite loop we have to check context.Depth property.
- To run the plugin only once just add a condition context.Depth <1 then pass the control to your logic.
- Deploy/Registration
- Plugins are registered in CRM using Plugin Registration Tool by creating a connection to target environment.
- These Plugins and Steps are added to the CRM Solution for Deployment in Upstream environments.
- Debugging, attach process
- To Debug Plugin we have to attach the process called as w3wp.exe and giving breakpoint to debug line by line.
- For Custom Workflow or Async Plugins attach CRMAsyncService.exe process
- Follow this article to know more about Plugin Debug.
- Remote Debugging
- Remote Debugging can also be followed.
- Follow this topic to understand the process of Remote Debugging.
- Plugin Profiler
- Using Plugin profiler we can debug our plugin. This can be done using Plugin registration tool.
- Follow this link to understand step by step methods using Plugin Profiler
- Developer Toolkit
- The Developer Toolkit is a set of Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 and Microsoft Visual Studio 2012 integration tools focused on accelerating the development of custom code for Microsoft Dynamics CRM. Read detail article here.
- Plugin Testing
- To test plugins personally I prefer to define some sample batch job to test if the codes written in the plugin works fine or not.
- There are also some frameworks available for testing Plugins like Fake XRM.
Release

- Adding in Solution
- Plugins and Steps are added to a solution for deployment.
- Exporting Solution
- From Development environment the solution should be exported for up-stream environment.
- Plugin Execution Order
- If multiple plugins are registered on the event of an entity then we can set the Execution order of the plugins to run one by one according to the need.
- If Execution orders are not specified then by default the plugins will run according to their registration date.
- Filtering Attributes
- When registering a plugin on an update message/event then it is best practice to specify the filtering attributes to trigger plugin otherwise the plugin will run on any field update which may cause unwanted issues.
Best Practice & Performance
- Async/Sync Consideration
- While developing plugins developers should validate the plugins if this runs synchronously or asynchronously.
- If synchronous then you have to consider the plugin to be light weight which runs faster otherwise timeout errors will be thrown.
- If Asynchronous plugin then we have to consider if there is any error then system job will capture the errors and users will not be notified immediately.
- Exception handling Consideration & Notification Service
- Handling exceptions in plugin is very important. Here i have written an article you can check for exception handling best practices in plugin.
- Infinite loop consideration
- Always check if your plugin runs infinite loop if so then use context depth to restrict this.
- Code optimization
- Write simple codes as much as possible.If we refer any external service then dont forget to close the connection. Dont use heavy weight objects causing the plugin slowdown.
- Performance optimization
- Developers must pay attention to optimize performance of plugins.
- I have written a best practice article here you can check.
Exception Handling
- Try Catch throw
- Always use try….catch block to catch specific runtime exceptions.
- Throw user understandable messages.
- Invalid Plugin Execution
- In Plugins always throw errors of type InvalidPluginExecution error.
- Logging system
- In Plugins we can use Error or Info Entities to log information.
- Tracing
- In Plugins we can specify tracing using ITracing interface.
- Window Event Viewer Entry
- Some runtime unhandled exceptions with detailed tracing are logged in windows event viewer.